The Primal Key: The Plight of the Plexus

In the realm of human physiology, there resides a complex network of nerves and tissues known as the plexus. These intricate structures serve as vital conduits for communication between the central nervous system and various parts of the body. However, when the plexus is compromised, a myriad of debilitating conditions can arise, profoundly impacting the quality of life. This article delves into the enigmatic world of the plexus, exploring its structure, functions, and the devastating consequences that can befall individuals when it malfunctions.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6530 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 261 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Unveiling the Anatomy of the Plexus
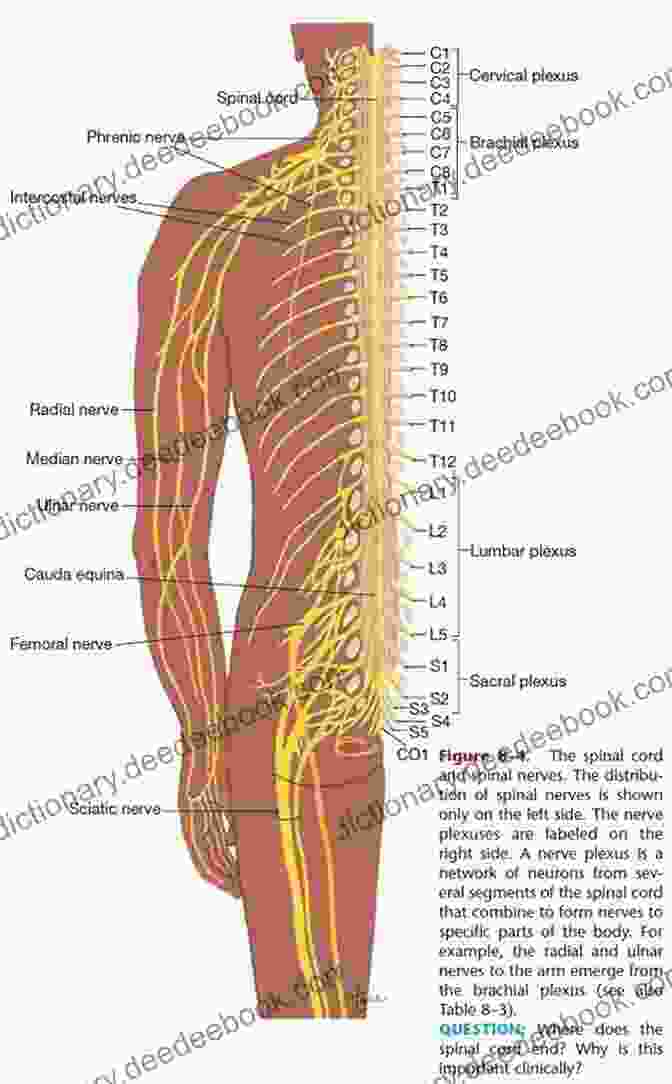
The plexus is formed by the intricate convergence of nerve fibers from multiple spinal cord segments. These nerve fibers intertwine to create a complex meshwork of connections, resembling a vast network of interconnected pathways. The plexus can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Spinal nerve plexus: Located in the peripheral nervous system, the spinal nerve plexus is found in the neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. It comprises nerve fibers from specific spinal cord segments and gives rise to nerves that innervate various body regions.
- Autonomic nervous system plexus: The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure. The ANS plexus is formed by nerve fibers from the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS and innervates organs and tissues throughout the body.
Exploring the Vital Functions of the Plexus
The plexus plays a pivotal role in a multitude of physiological processes:
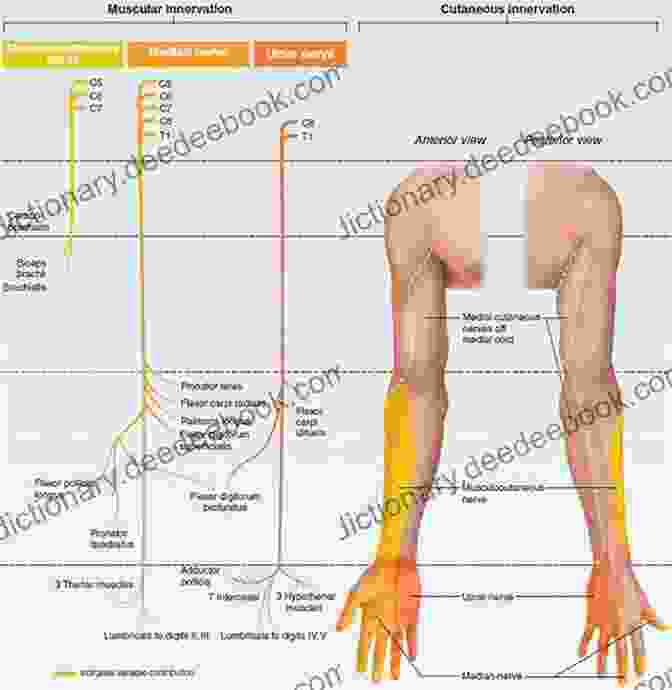
- Motor functions: The plexus transmits motor signals from the spinal cord to muscles, enabling voluntary movement and coordination.
- Sensory functions: Nerve fibers within the plexus convey sensory information from the body's surface and internal organs to the spinal cord and brain, allowing us to perceive sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature.
- Autonomic functions: The ANS plexus regulates involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure, maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of our internal organs.
The Devastating Impact of Plexus Dysfunction
When the plexus is compromised, it can lead to a range of debilitating conditions that can profoundly impact an individual's physical, emotional, and social well-being. These conditions may arise from trauma, infections, tumors, or congenital abnormalities.
Types of Plexus Disorders
Plexus disorders can affect different regions of the body, giving rise to specific symptoms and impairments:
- Brachial plexus injury: Damage to the brachial plexus, located in the neck, can result in weakness or paralysis of the arm, shoulder, and hand, as well as sensory disturbances in these areas.
- Lumbosacral plexus injury: This type of injury affects the lumbosacral plexus in the lower back and can lead to leg weakness or paralysis, foot drop, and bowel or bladder dysfunction.
- Autonomic nervous system dysfunction: Damage to the ANS plexus can disrupt the regulation of involuntary bodily functions, causing problems with heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and other autonomic functions.
Symptoms of Plexus Disorders
The symptoms of plexus disorders vary depending on the location and severity of the injury or dysfunction:
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Sensory disturbances (numbness, tingling, burning pain)
- Pain
- Difficulty with movement and coordination
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction
- Autonomic dysfunction (e.g., heart rate irregularities, excessive sweating)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Plexus Disorders
Diagnosing plexus disorders typically involves a comprehensive physical examination, a detailed medical history, and electrodiagnostic testing (e.g., nerve conduction studies, electromyography). Treatment strategies vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition, and may include:
- Rest and immobilization
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation
- Medications (e.g., pain relievers, muscle relaxants)
- Surgery (in some cases)
Living with Plexus Disorders
Living with a plexus disorder can be challenging, but there are strategies that can help individuals cope with the physical and emotional challenges they face:
- Seeking support: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and a sense of community.
- Adaptive technology: Utilizing assistive devices and adaptive technology can enhance independence and improve daily functioning.
- Self-care: Engaging in self-care practices such as exercise, meditation, and healthy eating can promote overall well-being.
- Education: Understanding the condition and its potential impact can empower individuals to advocate for their needs.
The plexus, an intricate network of nerves and tissues, plays a vital role in our physical and autonomic functions. When the plexus is compromised, a range of debilitating conditions can arise, significantly impairing individuals' quality of life. However, with proper diagnosis, treatment, and adaptive strategies, individuals can learn to live fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by plexus disorders. Continued research and advancements in medical care hold promise for improving outcomes and enhancing the well-being of those affected by these complex conditions.

5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6530 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 261 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Novel
Novel Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Bookmark
Bookmark Glossary
Glossary Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Library card
Library card Biography
Biography Memoir
Memoir Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Dictionary
Dictionary Thesaurus
Thesaurus Narrator
Narrator Character
Character Librarian
Librarian Catalog
Catalog Archives
Archives Periodicals
Periodicals Study
Study Research
Research Scholarly
Scholarly Academic
Academic Journals
Journals Reading Room
Reading Room Rare Books
Rare Books Special Collections
Special Collections Interlibrary
Interlibrary Literacy
Literacy Thesis
Thesis Awards
Awards Brianne Donaldson
Brianne Donaldson James Alan Sturtevant
James Alan Sturtevant Elizabeth George
Elizabeth George Swiss Chris
Swiss Chris Teagan Hunter
Teagan Hunter Ben Curtis
Ben Curtis Kathryn Ann Kingsley
Kathryn Ann Kingsley Harvey Phillips
Harvey Phillips Rosie May Garrett
Rosie May Garrett Otura Mercy
Otura Mercy Andrew James
Andrew James J Bartholomew Hivemind
J Bartholomew Hivemind Anthony James
Anthony James Jennifer Ann Bailey
Jennifer Ann Bailey Ron Roecker
Ron Roecker Toni Cade Bambara
Toni Cade Bambara Leonardo De Marchi
Leonardo De Marchi Nancy J Parezo
Nancy J Parezo Mrs O F Walton
Mrs O F Walton William Winter
William Winter
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 William GoldingThe Harrowing Tale of a Plague Survivor: A Medieval Epic of Resilience and...
William GoldingThe Harrowing Tale of a Plague Survivor: A Medieval Epic of Resilience and...
 Raymond ChandlerThe Four Pillars of Campaign Victory: A Comprehensive Guide to Winning...
Raymond ChandlerThe Four Pillars of Campaign Victory: A Comprehensive Guide to Winning... Finn CoxFollow ·14.3k
Finn CoxFollow ·14.3k Fletcher MitchellFollow ·12.3k
Fletcher MitchellFollow ·12.3k Gordon CoxFollow ·13.9k
Gordon CoxFollow ·13.9k Blake KennedyFollow ·3.6k
Blake KennedyFollow ·3.6k Henry Wadsworth LongfellowFollow ·13.8k
Henry Wadsworth LongfellowFollow ·13.8k Andy ColeFollow ·2.7k
Andy ColeFollow ·2.7k Rick NelsonFollow ·18k
Rick NelsonFollow ·18k Phil FosterFollow ·3.5k
Phil FosterFollow ·3.5k

 Jerome Powell
Jerome PowellBarbara Randle: More Crazy Quilting With Attitude -...
A Trailblazing Pioneer in...

 Jan Mitchell
Jan MitchellLapax: A Dystopian Novel by Juan Villalba Explores the...
In the realm of dystopian literature, Juan...

 Rodney Parker
Rodney ParkerOur Mr. Wrenn: The Romantic Adventures of a Gentle Man
Our Mr. Wrenn is a 1937 novel...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6530 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 261 pages |
| Lending | : | Enabled |